
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Science, Minzu University of China, Beijing 100081, China
2 Key Laboratory of Advanced Optoelectronic Quantum Architecture and Measurement (Ministry of Education), Beijing Key Laboratory of Nanophotonics & Ultrafine Optoelectronic Systems, and School of Physics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
3 Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
4 e-mail: hlguo@muc.edu.cn
5 e-mail: jiafangli@bit.edu.cn
Plasmonic sensing technology has attracted considerable attention for high sensitivity due to the ability to effectively localize and manipulate light. In this study, we demonstrate a refractive index (RI) sensing scheme based on open-loop twisted meta-molecule arrays using the versatile nano-kirigami principle. RI sensing has the features of a small footprint, flexible control, and simple preparation. By engineering the morphology of meta-molecules or the RI of the ambient medium, the chiral surface lattice resonances can be significantly enhanced, and the wavelength, intensity, and sign of circular dichroism (CD) can be flexibly tailored. Utilizing the relation between the wavelength of the CD peak and the RI of the superstrate, the RI sensor achieves a sensitivity of 1133 nm/RIU. Additionally, we analyze these chiroptical responses by performing electromagnetic multipolar decomposition and electric field distributions. Our study may serve as an ideal platform for applications of RI measurement and provide new insights into the manipulation of chiral light–matter interactions.
Photonics Research
2024, 12(2): 218
多波段激光合束技术在光电对抗领域的应用越来越受到重视,基于此提出了一种使用折射棱镜组的多波段激光合束方法,优选了牌号依次为H-ZLaF92、D-ZLaF85LS、H-ZBaF21的3种火石玻璃作为棱镜材料,通过对棱镜组的顶角值、入射角度以及位置关系的计算和仿真,设计了包含调整镜组、折射棱镜组、反射镜组和偏振滤光片的合束方案,同时利用将单一线性偏振激光束电矢量方向调整为平行于入射面的方法减小反射损耗。分析计算表明:在波长分别为550 nm、1060 nm、2000 nm情况下,入射角分别选择63.05°、61.35°、59.58°,3种材料的棱镜顶角值分别取51°、55°、60°;在光斑间距ΔX1、ΔX2分别为10 mm、20 mm的情况下,3种材料对应棱镜的远表面距离D、近表面距离d分别为289 mm、83.5 mm,366.4 mm、107.7 mm,381.6 mm、103.6 mm;在不进行光学镀膜的情况下,仅使用单一线性偏振光以布儒斯特角入射,也能够达到92.8%~97.6%的合束效率,与现有多波段合束技术相比,在成本方面有巨大的优势。
激光合束 多波段合束 折射棱镜 p偏振 合束效率 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(17): 1714002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, NE 68588-0511, United States of America
2 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 1037 Luoyu Road, Wuhan 430074, People’s Republic of China
3 School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology,Beijing, 100081, People’s Republic of China
4 Institut de Chimie de la Matière Condensée de Bordeaux, Avenue du Docteur Albert Schweitzer, F-33608 Pessac Cedex, France
Three-dimensional (3D) electrically conductive micro/nanostructures are now a key component in a broad range of research and industry fields. In this work, a novel method is developed to realize metallic 3D micro/nanostructures with silver-thiol-acrylate composites via two-photon polymerization followed by femtosecond laser nanojoining. Complex 3D micro/nanoscale conductive structures have been successfully fabricated with ~200 nm resolution. The loading of silver nanowires (AgNWs) and joining of junctions successfully enhance the electrical conductivity of the composites from insulating to 92.9 Sm-1 at room temperature. Moreover, for the first time, a reversible switching to a higher conductivity is observed, up to ~105Sm-1 at 523 K. The temperature-dependent conductivity of the composite is analyzed following the variable range hopping and thermal activation models. The nanomaterial assembly and joining method demonstrated in this study pave a way towards a wide range of device applications, including 3D electronics, sensors, memristors, micro/nanoelectromechanical systems, and biomedical devices, etc.
precise assembly joining silver nanowires nanofabrication three dimensional International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing
2019, 1(2): 025001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710119, China
3 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, Nebraska 68588-0511, USA
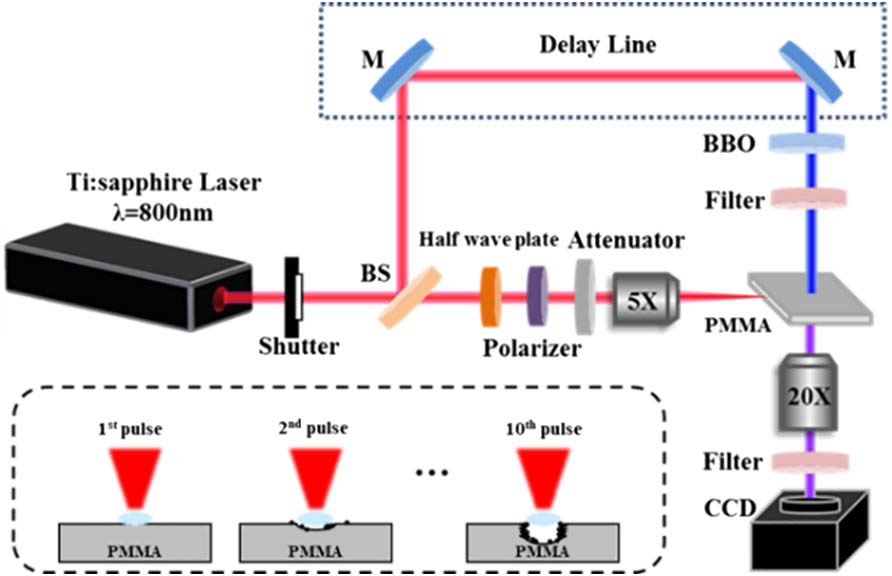
Cylindrical shockwaves inside polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) generated simultaneously with two hemispherical shockwaves induced by a femtosecond Gaussian beam laser were investigated using an ultrafast pump–probe imaging technique. The evolutions of these three shockwaves with probe delay and incident pulse number have been systematically analyzed. The plasma intensity and filament length in the center of cylindrical shockwave both decayed with pulse number. Moreover, the self-focused filament moved downstream towards the output surface with an increased pulse number. The experimental results and mechanism illustrated that energy deposition was suppressed by a degraded nonlinear effect due to a pre-ablated structure in multi-pulse irradiation.
140.7090 Ultrafast lasers 320.7120 Ultrafast phenomena 350.5400 Plasmas 350.3390 Laser materials processing Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(8): 081405
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Vibration and Noise Control Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
3 School of Optoelectronics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
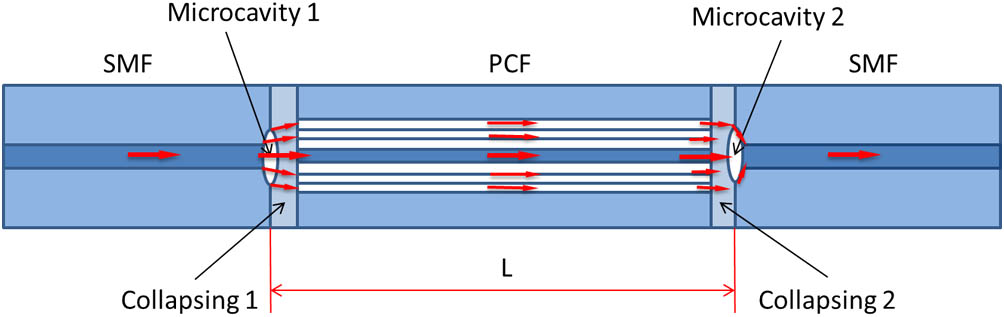
We propose a temperature-insensitive refractive index (RI) fiber sensor based on a Mach–Zehnder interferometer. The sensor with high sensitivity and a robust structure is fabricated by splicing a short photonic crystal fiber (PCF) between two single-mode fibers, where two microcavities are formed at both junctions because of the collapse of the PCF air holes. The microcavity with a larger equatorial dimension can excite higher-order cladding modes, so the sensor presents a high RI sensitivity, which can reach 244.16 nm/RIU in the RI range of 1.333–1.3778. Meanwhile it has a low temperature sensitivity of 0.005 nm/°C in the range of 33°C–360°C.
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(2): 020603
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Laser Thermal Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720, USA
3 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, Nebraska 68588-0511, USA
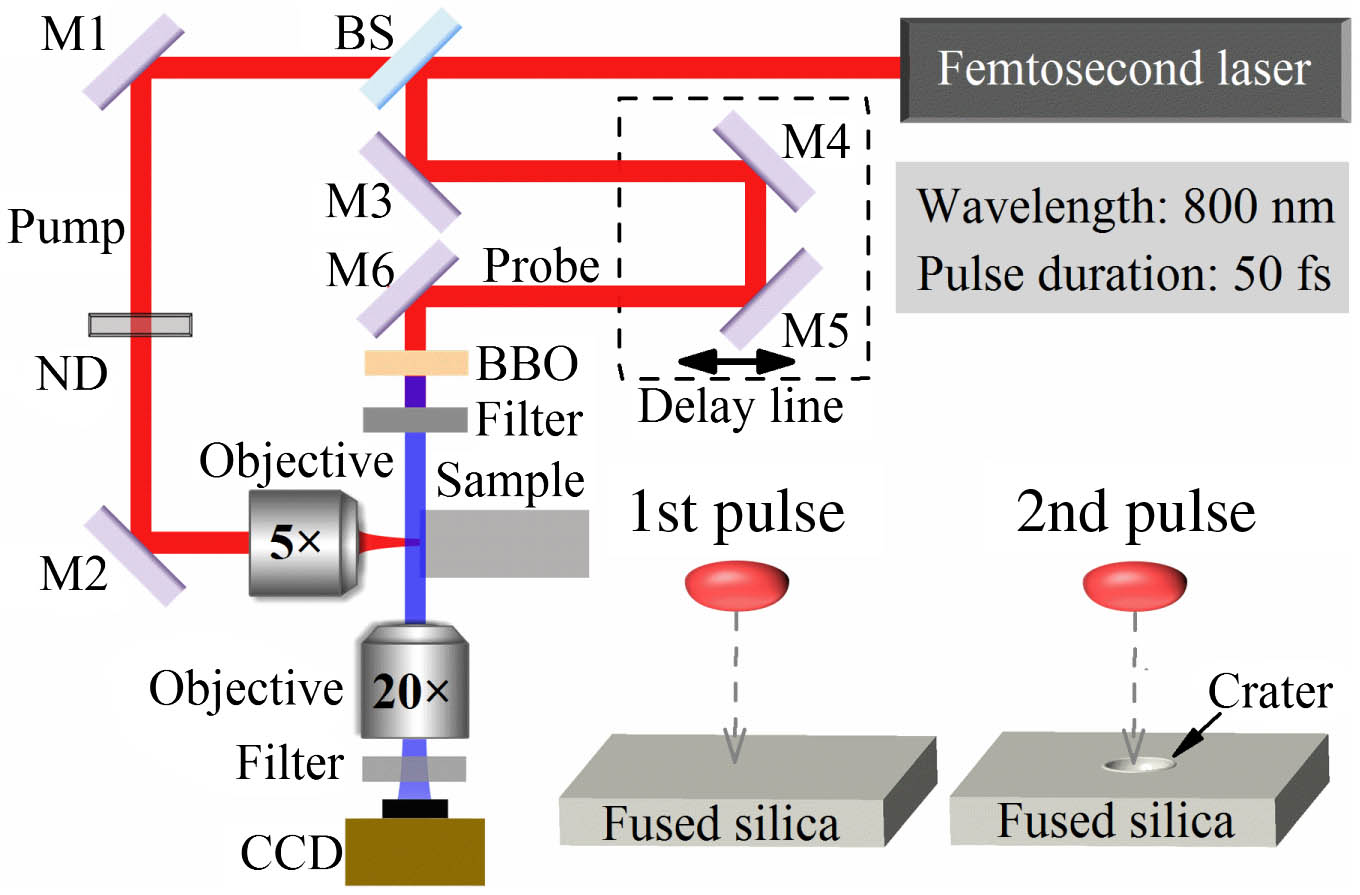
The dynamics of plasma and shockwave expansion during two femtosecond laser pulse ablation of fused silica are studied using a time-resolved shadowgraph imaging technique. The experimental results reveal that during the second pulse irradiation on the crater induced by the first pulse, the expansion of the plasma and shockwave is enhanced in the longitudinal direction. The plasma model and Fresnel diffraction theory are combined to calculate the laser intensity distribution by considering the change in surface morphology and transient material properties. The theoretical results show that after the free electron density induced by the rising edge of the pulse reaches the critical density, the originally transparent surface is transformed into a transient high-reflectivity surface (metallic state). Thus, the crater with a concave-lens-like morphology can tremendously reflect and refocus the latter part of the laser pulse, leading to a strong laser field with an intensity even higher than the incident intensity. This strong refocused laser pulse results in a stronger laser-induced air breakdown and enhances the subsequent expansion of the plasma and shockwave. In addition, similar shadowgraphs are also recorded in the single-pulse ablation of a concave microlens, providing experimental evidence for the enhancement mechanism.
(320.7100) Ultrafast measurements (140.3390) Laser materials processing (140.3440) Laser-induced breakdown. Photonics Research
2017, 5(5): 05000488
1 华中科技大学武汉光电国家实验室, 湖北 武汉 430074
2 美国内布拉斯加林肯大学电子工程系, 林肯 68503, 美国
3 北京理工大学机械与车辆学院, 北京 100081
介绍了碳纳米管(CNTs)/聚合物复合材料分散性、定向排布和组装方面的研究进展, 并利用双光子聚合(TPP)激光直写技术, 实现了多壁碳纳米管(MWNTs)在三维空间的定向排布和分子组装。通过加入硫醇分子, 提升了MWNTs/聚合物复合材料中CNTs的分散性和掺杂浓度, 增强了CNTs/聚合物复合材料在电学、光学、力学方面的性能, 并成功实现了三维CNTs功能器件的制造。研究结果表明, 通过将TPP激光直写技术与热退火工艺相结合, 可以实现对CNTs簇排列方向和位置的精确控制。
激光制造 三维微纳制造 碳纳米管 双光子聚合 飞秒激光直写
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
An optical fiber extrinsic Fabry–Perot interferometer (EFPI) is designed and fabricated for refractive index (RI) sensing. To test the RI of liquid, the following two different methods are adopted: the wavelength tracking method and the Fourier-transform white-light interferometry (FTWLI). The sensitivities of sensors with cavity lengths of 288.1 and 358.5 μm are 702.312 nm/RIU and 396.362 μm/RIU, respectively, by the two methods. Our work provides a new kind of RI sensor with the advantages of high sensitivity, mechanical robustness, and low cross sensitivity to temperature. Also, we provide a new method to deal with gold film with a femtosecond laser.
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(2): 020602
大连大学 环境与化学工程学院, 辽宁 大连 116622
将CD光盘的聚碳酸酯基底纳米条纹作为光子晶体传感器,考察了其传感性质。在40~120 ℃温度范围内,CD光子晶体的反射光谱强度由64.5%上升到99.1%,且温度与反射光谱强度的变化呈线性响应,相关系数R2为0.999 5。结果表明,该聚碳酸酯光子晶体膜可以作为温度传感器。另外,还考察了不同的有机醇对传感器的反射光谱强度的影响。发现在甲醇中,最大反射率与作用时间呈线性关系,在乙醇、正丙醇、正丁醇中也有同样的规律,不同醇的介电常数与反射光谱强度也有线性关系,表明本传感器还可以作为醇的检测手段。
CD光盘 光子晶体 传感器 CD disks photonic crystal sensor

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano-Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, Nebraska 68588-0511, USA
A simple and repeatable method to fabricate high-aspect-ratio (HAR) and high-quality microgrooves in silica is reported. The method consists of two steps: (1) formation of laser-modified regions by femtosecond Bessel beam irradiation, and (2) removing laser-modified regions through HF etching. Uniform, straight microgrooves can be fabricated and the highest aspect ratio that can be reached is ~52. The phenomenon is attributed to the uniform energy distribution in the long propagation distance, which leads to the long and uniform laser-modified regions and subsequent HF acid etching of laser-modified regions with high selectivity. This method will have potential applications in fabrication of HAR microgrooves in transparent materials.
140.3390 Laser materials processing 230.4000 Microstructure fabrication 320.5540 Pulse shaping Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(4): 041405





